Underactive Thyroid Can Be Difficult to Diagnose
Colorado Thyroid Disease Prevalence Study
Colorado Statewide health fair in 1995 looked at 25,862 participants to assess thyroid function. Participants responded to a 14-question hypothyroid symptom questionnaire, which was based on results from a previous study.1
Pinch to zoom
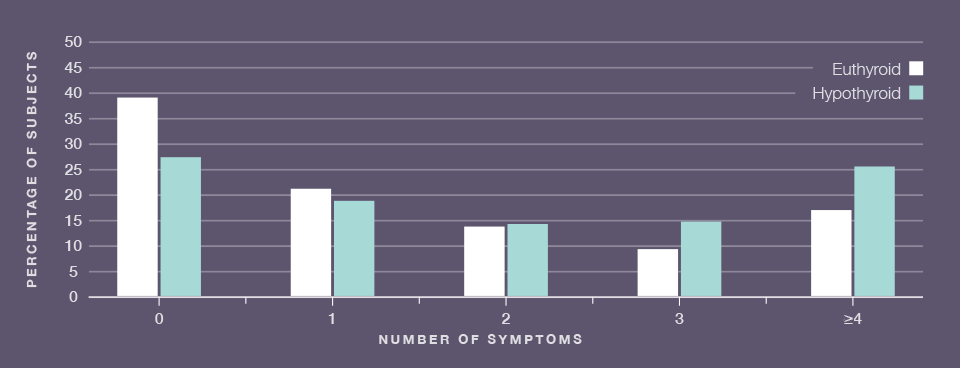
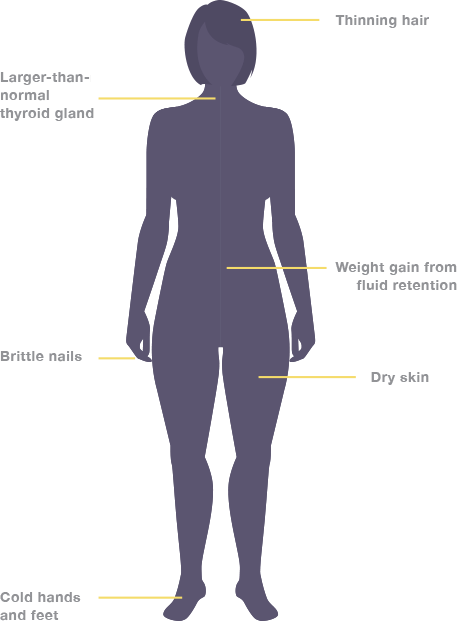
- Patients may not have signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism and, as a result, may not be properly diagnosed1
- Symptoms of underactive thyroid can be mild, vague, or easily confused with those of other diseases (eg, depression)2
- At times, symptoms may be assumed to be a part of the natural process of aging2